|
Project 1: Design, synthesis and characterization of multifunctional small molecules and polymers for surface functionalization.
To a very large extent, the surface properties of solid materials dictate their properties in the final application. The covalent immobilization of bioactive compounds onto solid surface has seen rapid growth in the past decade in such as biomedical, textiles, microelectronics, bioprocessing and food packaging. While the method of surface functionalization varies with each application, development of multifunctional linkers gain great attention. Its advantages include high specificity, nearly quantitative with mild ambient condition and simple workflow. By using multifunctional small molecules or polymers, surface functionalization can be done in one step with high fidelity.
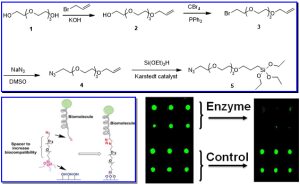
Figure 1. Synthesis of bifunctional silane and application for manufacture of peptide microarray
Project 2: Development of organic, inorganic and organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials with controlled sizes and functions by green chemistry
Due to small size, nanomaterials are found to show unusual properties comparing to their counterparts in bulk. There are great interests to develop new schemes to prepare functional nanoparticles, hybrid nanostruction and assemblies with appealing optical properties for a wide range of application. One example is the synthesis of ultrasmall gold nanoclusters with fluorescent emission using green chemistry. The other example is synthesis of nanoparticles with near-IR absorptions.

Figure 2. Synthesis of ultrasmall gold nanoclusters with fluorescent emission by green chemistry
Project 3: Application of bioconjugation / nanomaterials as chemical tools for sensing, imaging, diagnostics and therapy of human diseases like cancer.
The multifunctional properties of nanoparticles provide unique advantages for the specific delivery of imaging and therapeutic agents. Several ligands with sensing, imaging, diagnostics and therapy can be incorporated across the large nanoparticle surface area in a single nanoparticles system. Compare to small molecule ligands, nanomaterials can convey three benefits: a) Nanoparticles tend to accumulate in tumor tissue much more than they do in normal tissues through the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. b) Multivalent targeting significantly increases the binding affinity of a particle toward a target cell. c) Nanoparticle increase the blood circulation time by avoiding renal excretion. I am going to develop new chemical tools to tackle current problems in biomedical research which is otherwise inaccessible using traditional biological techniques.
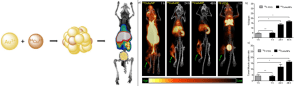
Figure 3. Gold-copper alloy nanoparticles for imaging
|
-
Liu, Y.; Li, W,; Luehmann H.; Zhao, Y. F.; Detering, L.; Sultan, D. E.; Hsiao, H. M.; Krupnick, A. S.; Gelman, A. E.; Combadiere, C.; Gropler, R. J.; Brody. S. L.; Kreisel, D. “Noninvasive Imaging of CCR2+ Cells in Ischemia Reperfusion Injury after Lung Transplantation” American Journal of Transplantation, in press
-
Zhao, Y. F. ; Detering, L.; Sultan, D.; Cooper M. L.; You, M.; Cho, S.; Meier, S. L.; Luehmann, H.; Sun, G.; Rettig, M.; Dehdashti, F.; Wooley, K. L.; Dipersio, J. F.; Liu Y. “Gold Nanoclusters Doped with 64Cu for CXCR4 Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Breast Cancer and Metastasis”, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 5959–5970
-
Pang, B§.; Zhao, Y. F. §; Luehmann, H.; Yang, X.; Detering, L.; You, M.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Ren Q.; Liu Y.; Xia, Y. “64Cu-Doped PdCu@Au Tripods: A Multifunctional Nanomaterial for Positron Emission Tomography and Image-Guided Photothermal Cancer Treatment”, ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 3121-3131 (§ Co-first authors)
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Pang, B.; Luehmann, H.; Detering, L.; Yang, X.; Sultan, D.; Harpstrite, S.; Sharma, V.; Cultler, C.; Xia, Y.; Liu Y. “Gold Nanoparticles Doped with 199Au Atoms and Their Use for Targeted Cancer Imaging by SPECT”, Advanced Health Materials, 2016, 5, 928-935
-
Kazuma, S.; Sultan, D.; Zhao, Y. F.; Detering, L.; You, M.; Leuhmann, H.; Abdalla, D.; Liu, Y. “Recent Advances of Radionuclide-Based Molecular Imaging of Atherosclerosis”, Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2015, 21, 5267-5276
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Sultan, D.; Detering, L.; Luehmann, H.; Liu Y. “Facile Synthesis, Pharmacokinetic and Systemic Clearance Evaluation, and Positron Emission Tomography Cancer Imaging of 64Cu-Au alloy Nanoclusters”, Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 13501-13509
-
Black, K.; Wang, Y.; Luehmann, H.; Cai, X.; Xing, W.; Pang, B.; Zhao, Y. F.; Cutler, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y. “Radioactive 198Au-Doped Nanostructures with Different Shapes for in vivo Analyses of Their Biodistribution, Tumor Uptake, and Intratumoral Distribution”, ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 4385-4394
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Sultan, D.; Detering, L.; Cho, S.; Sun, G.; Pierce, R.; Wooley, K.; Liu, Y. “ Copper-64-alloyed gold nanoparticles for cancer imaging: improved radiolabel stability and diagnostic accuracy”, Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2014, 53, 156-159.
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Pirrung, M. C.; Liao, J. “A Fluorescent Amino Acid Probe to Monitor Efficiency of Peptide Conjugation to Glass Surfaces for High Density Microarrays”, Molecular BioSystems 2012, 8, 879-887.
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Liu, Y.; Lee, I.; Song, Y.; Qin, X.; Zaera, F.; Liao, J. “Chemoselective fabrication of high density peptide microarray by hetero-bifunctional tetra(ethylene glycol) linker for click chemistry conjugation”, Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, Part A, 2012, 100, 103-110.
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Liao, J. “Feasible Synthesis of the GPR40 Antagonist by Constructing 2-Thiouracil Ring via Acid Mediated Cyclization”, Heterocycles 2011, 83, 1145-1151.
-
Liu, X. B.; Zhao, Y. F.; Chen, E. Q.; Ye, C.; Shen, Z. H.; Fan, X. H.; Cheng, S. Z. D.; Zhou, Q. F. “Lamella-to-lamella transition and effect of coil-stretching on crystallization in a rod-coil diblock copolymer containing poly (epsilon-caprolactone)”, Macromolecules 2008, 41, 5223-5229.
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Fan, X. H.; Wan, X. H.; Yi, Y.; Wang, L. S.; Dong, X.; Chen, X. F.; Zhou, Q. F. “Unusual phase behavior of a mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymers synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization ”, Macromolecules 2006, 39, 948-956.
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Fan, X. H.; Chen, X. F.; Wan, X. H.; Zhou, Q. F. “Synthesis and characterization of diblock copolymers based on crystallizable poly(ε-caprolactone) and mesogen-jacketed liquid crystalline polymer block”, Polymer 2005, 46, 5396-5405.
-
Zhao, Y. F.; Yi, Y.; Fan, X. H.; Chen, X. F.; Wan, X. H.; Zhou, Q. F. “Copolymers of 2,5-bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)oxycarbonyl]styrene with styrene and methyl methacrylate: synthesis, monomer reactivity ratios, thermal properties and liquid crystalline behavior”, J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Chem. 2005, 43, 2666-2674.
-
Gong, S. M.; Ma, H. Y.; Wan, X. H.; Zhao, Y. F.; He, J. Y.; Zhou, Q. F. “Synthesis and characterization of new cyno-group functionalized ionic liquids and their rheological properties”, Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities 2006, 27, 761-766.
-
Yi, Y.; Fan, X. H.; Zhao, Y. F.; Chen, X. F.; Wan, X. H.; Zhou, Q. F. “Atom transfer radical polymerization of 2,5-bis[(4-hexyloxyphenyl)oxycarbonyl]styrene”, Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2005, 23, 249-253.
-
Li, J. L.; Fan, X. H.; Zhao, Y. F.; Chen, X. F.; Wan, X. H.; Zhou, Q. F. “Synthesis and characterization of copolymer of 2,5-bis[(4-methoxyphenyl)-oxycarbonyl]styrene and styrene with high molecular weight”, Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2004, 22, 289-293.
|
 1400 J. R. Lynch Street, P.O. Box 17910
1400 J. R. Lynch Street, P.O. Box 17910



