Assignment 12 (Due: 04/21, by 11.59 PM) posted.
Assignment 13: Quiz (Due: 04/23, by 11.59 PM) posted in Canvas.
Reading List of Topics for Assignment 13 (Quiz to be posted in Canvas; will be due on 04/23, by 11.59 PM)
Take Home Exam 4 posted (also available in Canvas). Due in Canvas by April 28th, 11.59 PM for both graduating and non-graduating students.
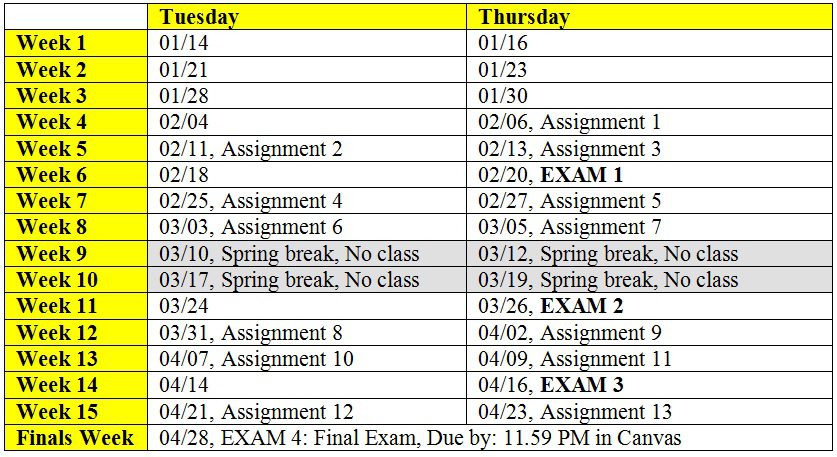
Check Assignment and Exam Schedules for the updated schedule of the course
—————————————————–
Dr. Meg's Desktop Selected Lecture Videos
—————————————————–
Syllabus
Amanuel Gebre: Mondays, Fridays: 10 AM to 3 PM; Wednesdays: 11 AM to 3 PM
Office Hours in Canvas: Meet the TA using the "Chat" feature in Canvas during the above timings
E-mail: J00801049@students.jsums.edu
Lecture Slides
Module 1: Algorithm Efficiency Analysis
Sample C++ Code and Explanation on dynamically creating and using a two-dimensional array
Module 6: P, NP, NP-Complete Problems
Question Bank
QB Module 1: Algorithm Efficiency Analysis
QB Module 2 – Classical Design Techniques
QB Module 4 – Dynamic Programming
QB Module 5 – Graph Theory Algorithms
Assignments
Check Canvas for the timer code.
Assignment 4 (Programming): Design and Implementation of a Θ(n) Algorithm to Determine the Most Frequently Occurring Integer in an Array of Integers
Check Canvas for the code.
Assignment 5 (Programming): Comparison of two Recursive Algorithms to Determine the Minimum Element in an Array
Check Canvas for the code.
Assignment 6 (Programming): Using the Merge Sort Algorithm to Determine the Number of Inversions and the Inverted Pairs of an Array
Check Canvas for the code.
Assignment 7 (Programming): Binary Search vs. Brute Force Search Algorithms for Finding a Local Minimum in a Two-Dimensional Array
Assignment 8 (Programming): Dynamic Programming Algorithm for Optimum Coin Collection in a Two-Dimensional Grid
Check Canvas for the sample C++ code to work with two-dimensional arrays.
Assignment 9 (Programming): Dynamic Programming-based Solution for the Longest Common Subsequence Problem
Assignment 10 (Programming): Dynamic Programming: Coin Change Problem
Check Canvas for the Code
Assignment 11 (Non-Programming-Take Home): Matrix Chain Multiplication (Submit a word or PDF version of the solutions in Canvas by April 9th, 11.59 PM.)
Assignment 12 (Non-Programming-Take Home): Prim's Minimum Spanning Tree Algorithm (Submit a PDF version of the solutions in Canvas by April 21st, 11.59 PM.)
Exams
Take Home Exam 2 (also available in Canvas). Due in Canvas by March 26th, 11.59 PM.
Take Home Exam 3 posted (also available in Canvas). Due in Canvas by April 16th, 11.59 PM.
Take Home Exam 4 posted (also available in Canvas). Due in Canvas by April 28th, 11.59 PM. For Graduating seniors, it is due on April 24th, 11.59 PM
Dr. Meg's Desktop Selected Lecture Videos (YouTube Links)
Module 1: Analyzing the Efficiency of Algorithms
Time-Complexity analysis of a recursive algorithm to compute the factorial of an integer
Example for solving recurrence relations
Time-complexity analysis of an iterative algorithm to determine whether an array has unique elements
Decrease and Conquer – Insertion Sort Algorithm and Examples
Module 2: Classical Algorithm Design Techniuqes
Brute Force Algorithms QB – String Matching Problems
Divide and Conquer – Theorem-Proof: In order Traversal of a Binary Search Tree
Divide and Conquer – Master Theorem
Binary Search Algorithm and Examples
Comparison of Bottom-up and Top-down Approaches for Heap Construction
Transform and Conquer – Proof for Euclid's GCD Formula
Transform and Conquer – Heap Sort
Space-Time Tradeoffs for the Sorting Algorithms (Merge, Insertion and Heap Sorts)
Module 3: Greedy Technique
Greedy Technique – Fractional Knapsack Problem
Greedy Technique – Huffman Codes (Variable Length Prefix-free Encoding)
Module 4: Dynamic Programming
Dynamic Programming: Coin-row Problem Discussion and Example
Dynamic Programming: Binomial Coefficient
Dynamic Programming Solution for the Coin Collecting Problem in a Two-Dimensional Grid
Dynamic Programming: Integer Knapsack Problem (0-1 Knapsack Problem)
Module 5: Graph Theory Algorithms
Depth First Search on Directed Graph
Depth First Search and Articulation Points
Breadth First Search and 2-Colorability of Graphs
Topological Sort on DAGs and Proof for Neccessary and Sufficient Condition
Dijkstra's Algorithm for Shortest Path Trees and Proof for Correctness
Bellman-Ford Algorithm for Shortest Path Trees and Examples New!!
Kruskal's Algorithm: Examples to find Minimum Spanning Trees
Kruskal's Algorithm: Proof of Correctness
Properties (1 and 2) of Minimum Spanning Tree: IJ-Cut and Minimum Weight Edge
Prim's Algorithm for Minimum Spanning Trees and Proof for Correctness
Floyd's All Pairs Shortest Paths Algorithm
Part 1 Part 2 Part 3 Part 4 Part 5 Part 6 Part 7
Module 6: P, NP and NP-Complete Problems
Polynomial Reduction: Hamiltonian Circuit to Traveling Salesman Problem
Polynomial Reductions: Independent Set, Clique and Vertex Cover
Multi-fragment Heuristic for the Traveling Salesman Problem